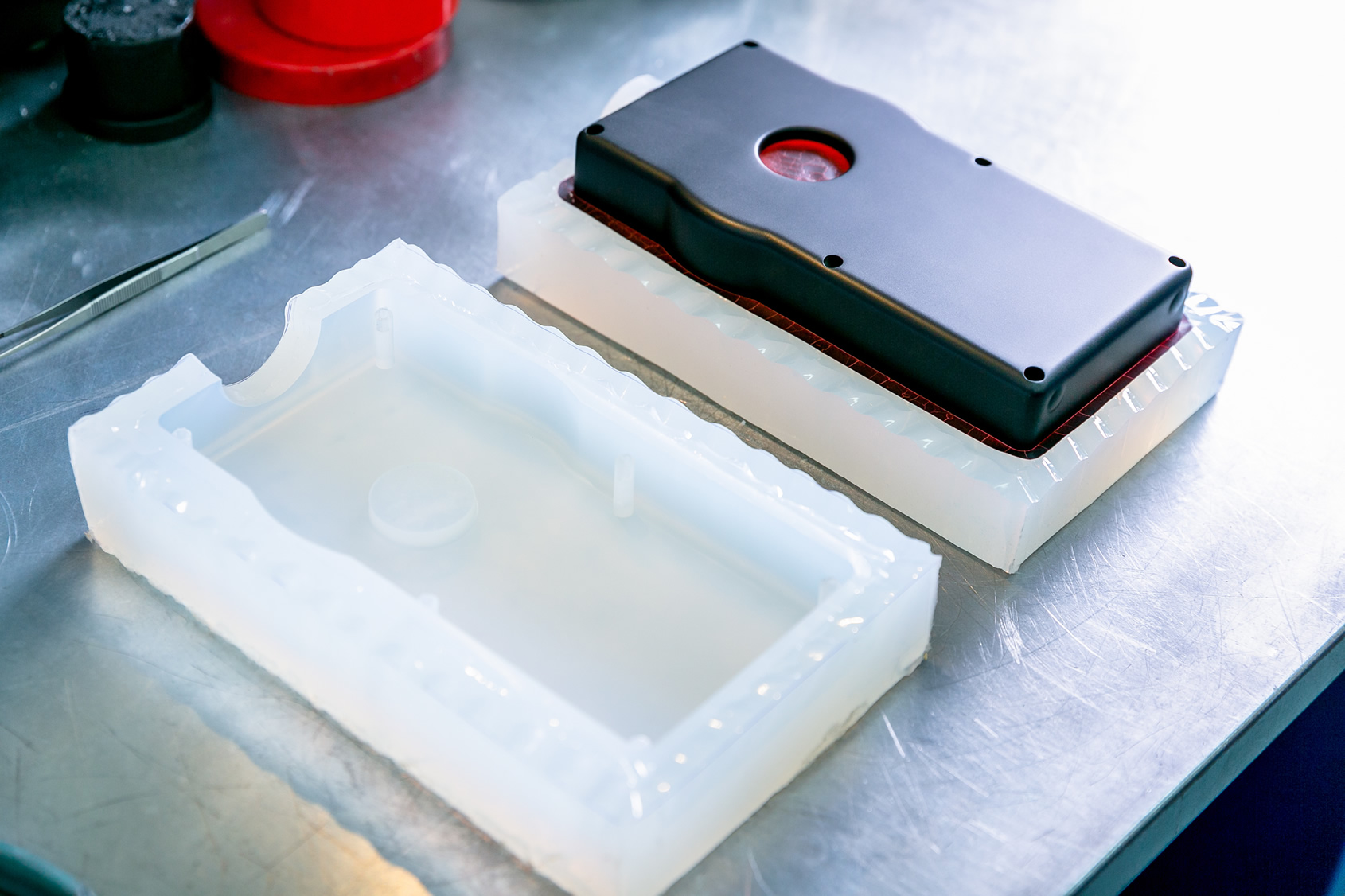
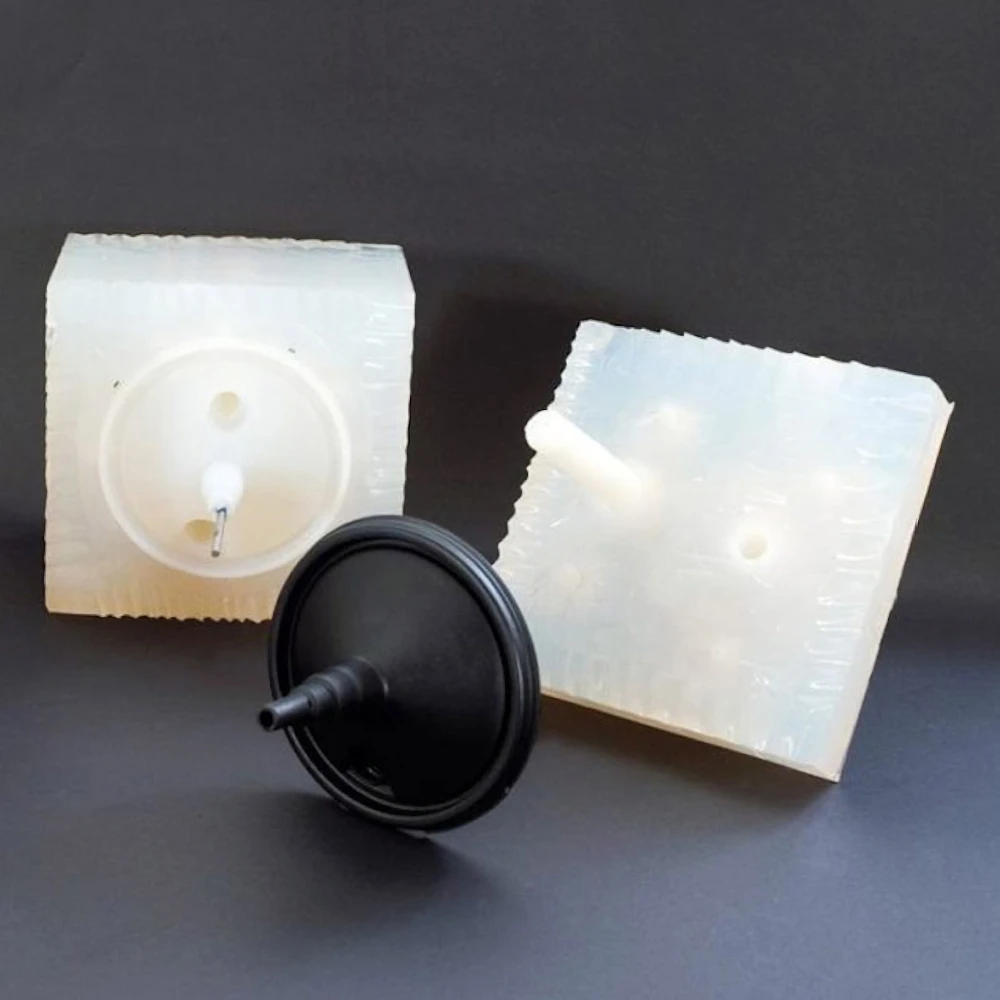
In today’s highly competitive markets — from consumer electronics to medical devices — speed is everything. Success often depends on how fast a concept can become a functional product ready for user testing or investor approval.
Silicone molding, also known as vacuum casting, has become a crucial bridge between rapid prototyping and mass production. It offers high-quality prototypes in a fraction of the time and cost of traditional injection molding.
This article explains how silicone molding accelerates product launch cycles while maintaining quality and flexibility.
What Is Silicone Molding?
Silicone molding is a low-volume manufacturing process that uses a silicone mold to cast parts — typically using polyurethane or elastomer resins — replicating the master model with high accuracy.
✔ Ideal for 10–50 units per mold
✔ mimics production materials (ABS-like, PP-like, soft rubber-like, clear plastic)
Typical Applications
-
Concept prototypes
-
Functional testing parts
-
User-evaluation models for investor presentations
-
Pre-production verification
Why Silicone Molding Is a Game-Changer
1. Short Lead Times
-
Silicone tooling: 2–5 days
-
Ready parts: within 7–10 days
-
Injection tooling comparison: 4–12 weeks
Up to 80% reduction in development time
2. Cost-Efficient Small Batch Manufacturing
| Volume Stage | Recommended Method | Tooling Cost | Part Cost | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–10 pcs | 3D Printing | Low | Moderate | Fast |
| 10–200 pcs | Silicone Molding | Low | Low | Fast |
| 1,000+ pcs | Injection Molding | High | Very Low | Slow to Start |
📌 Saves thousands in tooling during the prototype phase
3. Excellent Detail & Surface Quality
-
Replicates textures, sharp features, undercuts
-
Post-process options: painting, chroming, color matching, transparency
Tolerance capability
| Feature | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | ±0.10–0.30 mm |
| Wall Thickness | ≥1.0 mm recommended |
| Maximum Size | Up to 1,000 mm (depends on mold box) |
Equivalent to many CNC and injection-molded prototype quality levels.
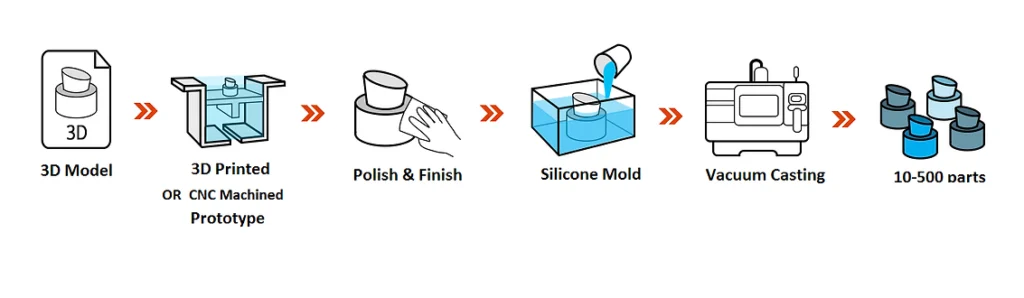
How Silicone Molding Works — Step by Step
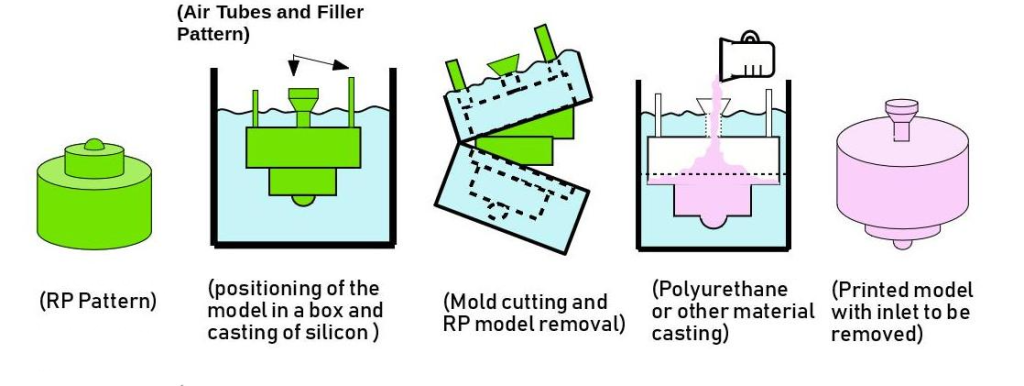

1. Master Model Creation
Usually done by CNC machining or high-resolution 3D printing.
2. Mold Fabrication
Silicone is poured over the master and cured (6–12 hours).
3. Cut & Split
The master is removed, forming the cavity.
4. Vacuum Casting of Parts
Resin is poured, air evacuated → bubble-free casting.
5. Curing + Finishing
Cleaning, trimming, coating, texture replication.
🔁 Each mold yields 10–50 high-quality parts
Silicone Molding vs. Injection Molding — Which to Choose?

| Feature | Silicone Molding (Vacuum Casting) | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Time | 7–10 days | 4–12 weeks |
| Tooling Cost | Low ($200–$2000) | High ($5,000–$50,000+) |
| Unit Volume | 10–200 pcs | 1,000–1,000,000+ pcs |
| Design Iteration Cost | Very Low | High |
| Surface Finish | Excellent | Excellent |
| Suitable For | Prototype & Pre-Series | Mass Production |
📌 Best strategy: Prototype with silicone molds → Scale with injection molds once design is validated
Industry Applications
| Industry | Components |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Interior trim, connectors, housings |
| Medical Devices | Enclosures, ergonomic handles, seals |
| Robotics | Soft components, flexible casings |
| Consumer Electronics | Wearable casings, buttons, transparent parts |
| Aerospace | Low-volume functional evaluations |
Case Insight:
A consumer electronics startup reduced their development cycle from 6 months → 2 months by swapping early injection tooling plans for silicone molding during testing.
How It Accelerates Time-to-Market
✅ Faster iterations → detect design flaws early
✅ Functional testing with near-production materials
✅ Real-user trials before large capital investment
✅ Enables early product launch strategy: pilot run → marketing → investor demos
Companies using silicone molding often cut development cost by 50% and launch 2–3× faster.
Best Practices for High-Quality Results
| Tip | Reason |
|---|---|
| Maintain 1.5–4 mm wall thickness | Prevent deformation & air traps |
| Add radii to sharp corners | Improve flow & durability |
| Choose resin that mimics final product | Better testing reliability |
| Plan for mold segmentation | Enables complex geometries |
Expert consultation early in design avoids expensive rework later.
Future Outlook
-
3D printed master tools for even faster turnaround
-
More sustainable polyurethane resins
-
Increased simulation accuracy → fewer iterations
-
Hybrid workflows combining CNC + Vacuum Casting + Injection Molding
Silicone molding is becoming a core link in digital rapid manufacturing ecosystems.
Conclusion
Silicone molding delivers:
✅ Production-like surface quality
✅ Low-cost small batches
✅ Rapid lead times for testing & validation
✅ Faster path from design → product launch
If your goal is better prototypes, faster — silicone molding is the perfect solution to accelerate your design-to-market timeline.
FAQs
What is silicone molding used for?
Silicone molding is mainly used for producing high-quality prototype parts and low-volume batches (10–200 pcs) that simulate the final production quality before mass manufacturing. It helps companies validate design, functionality, and market response quickly.
How long does the silicone molding process take?
Typical lead time is 7–10 days depending on part complexity:
-
Master model: 1–3 days
-
Silicone mold making: 2–3 days
-
Casting & finishing: 3–5 days
This is significantly faster than injection molding, which takes 4–12 weeks.
What materials can be used in silicone molding?
Silicone molds are most commonly used with polyurethane (PU) resins, which can simulate:
-
ABS-like / PP-like engineering plastics
-
Rubber-like elastomers (Shore A 30–90)
-
Transparent materials (PMMA-like)
-
Heat-resistant or flame-retardant materials (UL94 V-0)
How many parts can one silicone mold produce?
A silicone mold typically yields 10–50 castings depending on:
-
geometry sharpness
-
casting resin
-
curing temperature
-
surface finish needs
Larger or complex parts may reduce mold lifespan.
How accurate are silicone molded parts?
Dimensional tolerance ranges from ±0.10–0.30 mm, ideal for functional prototypes and cosmetic models. It can also capture fine textures, ribs, logos, and undercuts.
What industries benefit most from silicone molding?
-
Automotive and EV components
-
Medical device prototypes
-
Consumer electronics and wearables
-
Industrial machinery housings
-
Aerospace low-volume testing parts
Any industry requiring fast design validation benefits from silicone molding.
How does silicone molding compare to 3D printing?
| Feature | Silicone Molding | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Quality | Excellent | Good–moderate |
| Material Durability | High | Varies by process |
| Volume Efficiency | Best for 10–200 pcs | Best for 1–10 pcs |
| Lead Time | Fast | Fast |
| Cost per Unit | Lower at scale | Higher at scale |
Many teams 3D print the master model, then use silicone molding for batch production.
Can silicone molding produce production-grade parts?
While mainly for prototypes and pilot runs, materials can closely mimic production plastics. It is not ideal for long-term, high-temperature, or structural load-bearing applications compared to injection molding.
Can parts be colored, textured, or transparent?
✅ Yes. Silicone molding supports:
-
Pantone color matching
-
Semi-transparent or fully clear finishes
-
Glossy or textured surfaces
-
Chrome plating or painting
It’s great for display-ready prototypes.
When should I choose silicone molding instead of injection molding?
Choose silicone molding if you need:
✅ < 200 pcs
✅ Faster delivery for testing or marketing
✅ Frequent design changes
✅ Lower initial investment
If volume rises above 500–1,000 pcs, transition to injection molding becomes more cost-effective.