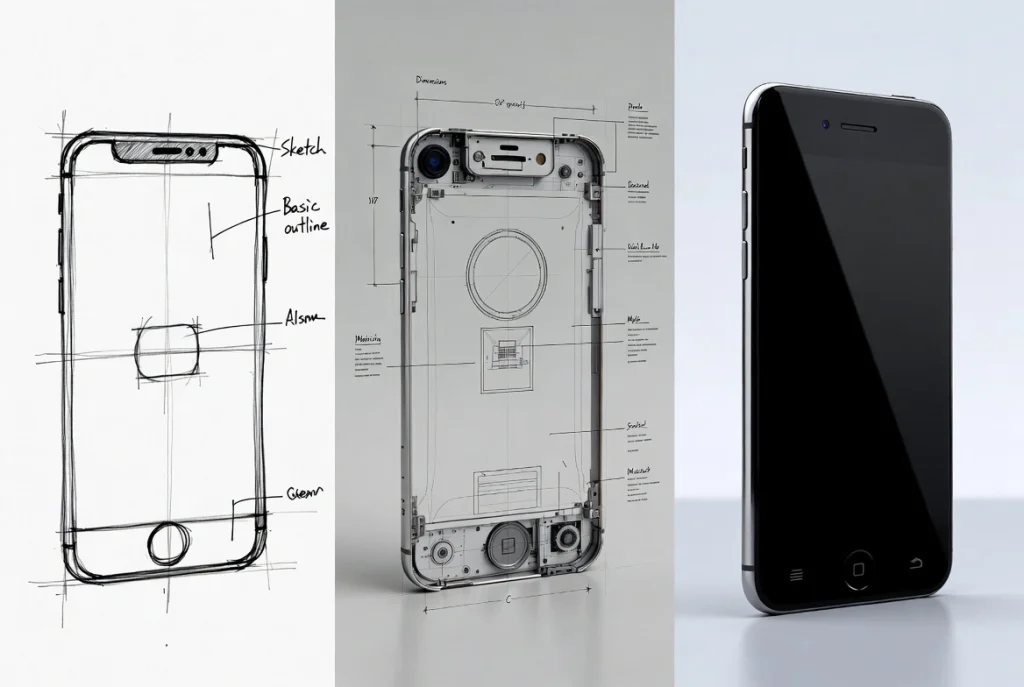
Few companies in the world combine art, technology, and engineering as seamlessly as Apple.
From the smooth aluminum unibody of a MacBook to the glossy finish of an iPhone, every Apple device begins as a precisely engineered prototype.
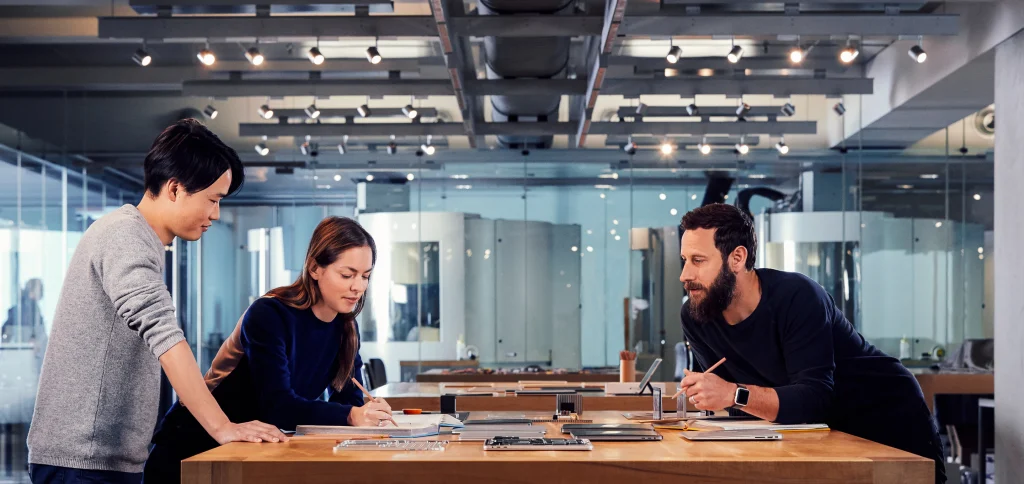
Behind the scenes, Apple secret to product excellence lies in its hardware prototyping ecosystem — a tightly integrated network of designers, machinists, and material scientists working together to turn ideas into reality in record time.
Why Hardware Prototyping Is Central to Apple Success
Apple product philosophy — “Design is how it works” — is realized through constant iteration and refinement.
Every iPhone button click, hinge feel, and metal curve is perfected through hundreds of CNC-machined prototypes before mass production begins.
| Prototype Type | Purpose | Typical Iterations |
|---|---|---|
| Concept Mockup | Ergonomic and visual validation | 10–20 |
| CNC Functional Prototype | Fit, assembly, material testing | 30–50 |
| Pre-Production Model | Factory process optimization | 5–10 |
💡 Each Apple device undergoes 50–80 design iterations before final approval.
Apple Hardware Prototyping Workflow
Apple prototyping pipeline blends digital simulation and physical fabrication, minimizing the gap between design intent and manufacturability.
Step 1 – Design & Simulation
-
Apple designers use Siemens NX, SolidWorks, and proprietary CAD tools.
-
Real-time simulation of stress, fit, and heat dissipation.
-
Cross-department collaboration between design, mechanical, and materials teams.
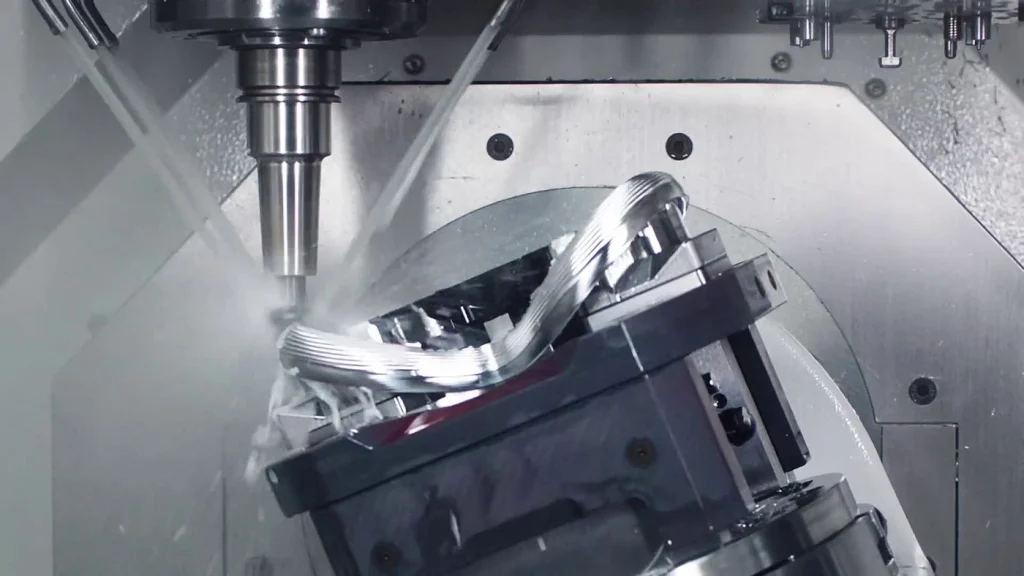
Step 2 – CNC Machining & Rapid Prototyping
-
Machining of aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and composite materials.
-
Multi-axis CNC machining centers achieve ±0.005 mm tolerances.
-
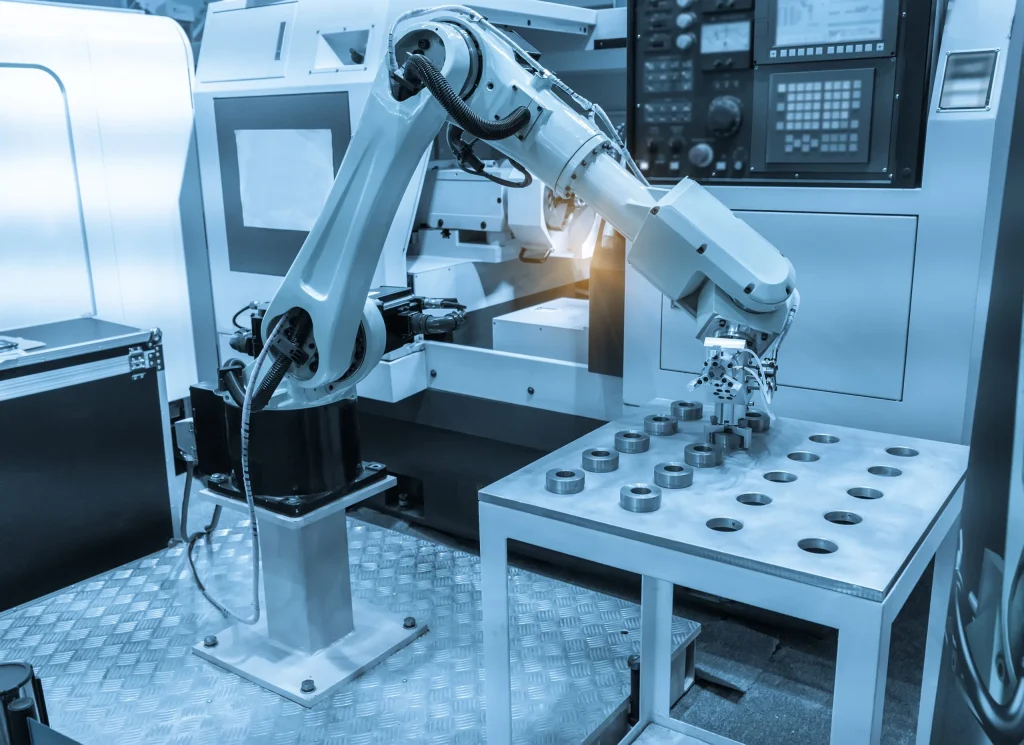
Robots handle overnight machining for non-stop iteration.
Step 3 – Surface Finishing & Assembly
-
Polishing, anodizing, and bead blasting ensure visual consistency.
-
Assemblies tested for tactile feel, hinge resistance, and button feedback.
Step 4 – Testing & Feedback
-
Each prototype is subjected to mechanical, thermal, and visual tests.
-
Digital measurement data immediately updates the CAD model.
| Workflow Stage | Duration | Accuracy | Key Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAD Design | 2–3 hrs | Virtual | Concept |
| CNC Machining | 6–12 hrs | ±0.005 mm | Functional part |
| Surface Finish | 3–6 hrs | Ra 0.2–0.4 µm | Visual quality |
| Testing & Feedback | 6 hrs | ±0.02 mm | Performance report |
🕒 Total iteration cycle: less than 24 hours.
Materials Behind Apple Precision
Apple doesn’t just choose materials for strength — it chooses them for emotion.
Every surface must feel premium, resist wear, and reflect light perfectly.
| Material | Used In | Why It’s Chosen |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum 6063 / 7075 | MacBook, iPhone chassis | Lightweight, strong, recyclable |
| Stainless Steel 316L | Apple Watch frame | Corrosion resistance, gloss finish |
| Titanium Alloy | Apple Watch Ultra | Strength-to-weight advantage |
| Ceramic & Glass | iPhone back, sensors | Sleek surface and durability |
| POM, ABS, PC | Internal components | Structural and electrical insulation |
💬 Apple recycles over 200,000 tons of aluminum annually in its closed-loop production system.
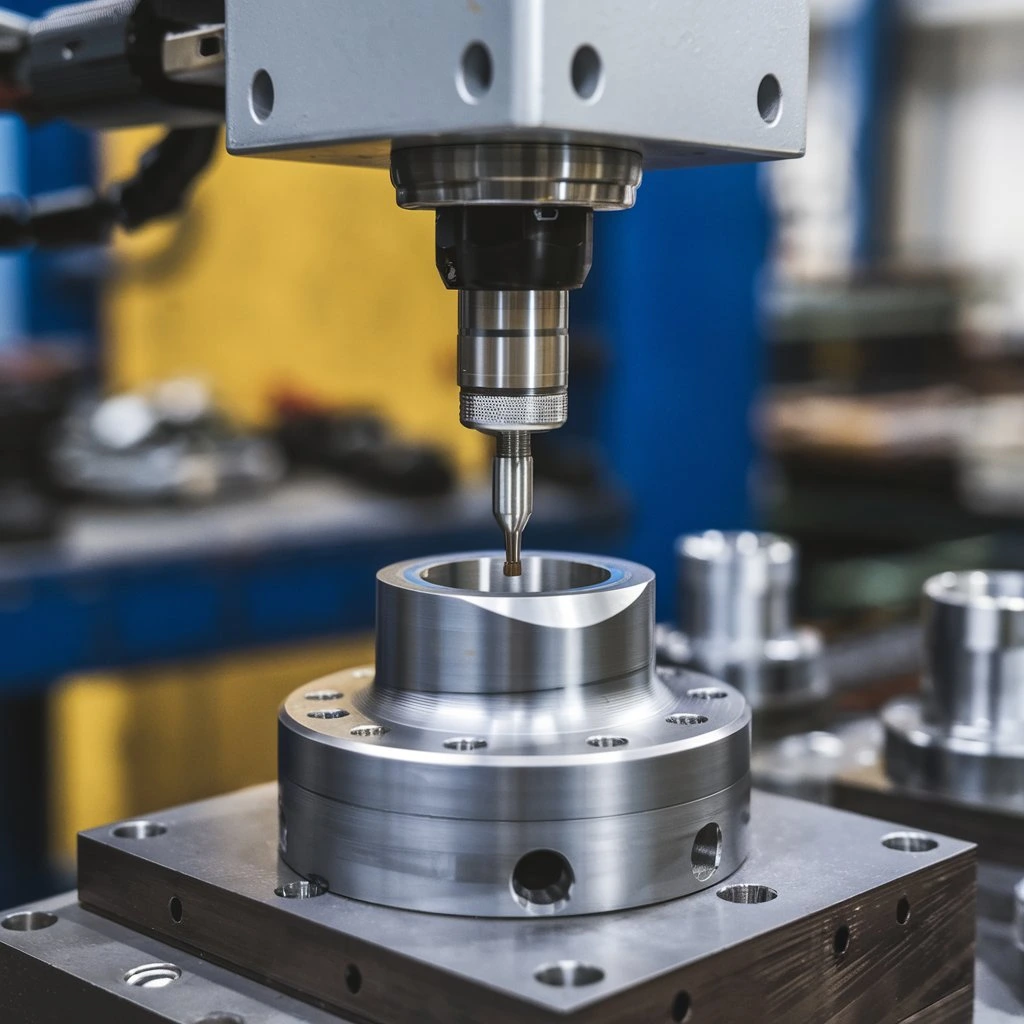
CNC Machining: Apple Precision Engine
Apple famous unibody design was made possible by 5-axis CNC machining — carving a laptop body from a single aluminum billet.
| Parameter | Apple CNC Standard |
|---|---|
| Tolerance | ±0.005 mm |
| Surface Roughness | Ra 0.2–0.4 µm |
| Machining Axis | 5-axis simultaneous |
| Measurement | CMM + laser scanner |
| Material Waste | <10% (optimized toolpath) |
💡 Over 10,000 CNC machines operate in Apple supplier network, producing parts with micron-level precision.
Surface Finishing and Aesthetic Perfection
Apple finishing processes are just as critical as machining itself.
Every prototype undergoes multiple surface treatments to achieve Apple signature look and feel.
| Finishing Type | Purpose | Process Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Bead Blasting | Uniform matte texture | 30–60 mins |
| Anodizing (Type II) | Color + corrosion protection | 3–5 hrs |
| Polishing | Gloss and tactile smoothness | 1–2 hrs |
| Brushing | Metallic grain alignment | 1 hr |
| Laser Engraving | Branding + serial marking | 30 mins |
📸 Apple finishing teams evaluate reflectivity and texture under different lighting conditions — down to the microscopic level.
Apple “Digital-to-Physical” Speed Advantage
Unlike traditional manufacturers, Apple prototyping and design teams work side-by-side in Cupertino and Shenzhen.
This co-location enables rapid iteration, instant decision-making, and same-day validation.
| Stage | Traditional Lead Time | Apple Lead Time |
|---|---|---|
| Design to Prototype | 3–5 days | 6–12 hours |
| Revision Cycle | 1 week | 24 hours |
| Validation Testing | 3 days | 1 day |
💡 Apple design loop is up to 5× faster than the industry average.
Design + Engineering Integration
Apple strength lies in uniting designers, machinists, and material scientists.
Every decision — from edge curvature to screw fitment — is validated in real-world tests.
-
CNC precision enables invisible seams and perfect symmetry.
-
Designers and engineers co-create tooling paths to achieve desired aesthetics.
-
Apple use of micron-level measurement tools ensures perfect alignment in assembly.
📏 Apple alignment tolerance for visible joints is less than 0.02 mm.
From Prototype to Production
Once a prototype meets Apple design standards, it transitions to low-volume pre-production.
Here, Apple tests manufacturing scalability and consistency.
| Phase | Objective | Partner |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Production | Validate assembly process | Foxconn / Pegatron |
| Pilot Run | Stress test design + tooling | Internal engineering |
| Mass Production | Volume scaling | Supplier factories |
🧠 Each production part is digitally verified against its prototype data file before shipment.
Why Apple Prototyping Culture Works
| Principle | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Integrated Design + Engineering | Rapid problem solving |
| In-House CNC and Finishing Labs | Confidentiality + control |
| Obsession with Detail | Perfect fit and feel |
| Constant Feedback Loop | Continuous refinement |
💬 Apple doesn’t just build prototypes — it builds perfection.
Lessons for Global Manufacturers
-
Treat prototyping as part of design, not a separate phase.
-
Invest in CNC precision for both functionality and appearance.
-
Shorten feedback loops with digital inspection tools.
-
Maintain tight tolerance and design integrity across teams.
-
Blend aesthetic and mechanical engineering — Apple greatest secret.
Conclusion
Apple hardware prototyping process is where precision meets imagination.
By merging 5-axis CNC machining, surface artistry, and rapid iteration, Apple has built a system that delivers both technical performance and emotional design appeal.
It’s not just how Apple designs — it’s how they engineer beauty, one micron at a time.
FAQs
What makes Apple hardware prototyping process unique?
Apple combines industrial design, mechanical engineering, and precision machining under one roof.
Unlike most manufacturers, Apple design and CNC teams collaborate directly — allowing design changes and prototype iterations to happen within hours, not weeks.
How many prototypes does Apple build before releasing a new product?
Each Apple product, such as the iPhone, MacBook, or Apple Watch, undergoes 50–80 prototype iterations.
This includes multiple material, machining, and finishing tests before final mass production.
What CNC technologies are used in Apple prototyping labs?
Apple uses 5-axis CNC machining centers, CNC EDM (electrical discharge machining), and CMM (coordinate measuring machines) for precision verification.
These systems achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm, ensuring every component fits perfectly.
What materials does Apple use for its prototypes?
Apple prototypes are made using high-performance and sustainable materials, including:
-
Aluminum 6063 / 7075 for MacBook and iPhone frames
-
Stainless Steel 316L for Apple Watch and structural parts
-
Titanium alloy for premium devices
-
Ceramics and reinforced glass for surface and aesthetic testing
How fast can Apple create a working hardware prototype?
Thanks to in-house CNC labs and automation, Apple can move from CAD design to functional prototype in 6–12 hours.
This enables daily iteration cycles and faster decision-making across design and engineering teams.
Why does Apple rely heavily on CNC machining?
CNC machining offers superior precision, repeatability, and surface quality compared to other rapid prototyping methods.
It’s ideal for metal components that require both functional strength and visual perfection, such as MacBook enclosures or iPhone frames.
What is the tolerance level of Apple machined parts?
Apple maintains ultra-precision tolerances in its prototypes:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | ±0.005 mm |
| Surface Roughness | Ra 0.2–0.4 µm |
| Alignment Tolerance | <0.02 mm |
| Repeatability | 99.98% |
These ensure a perfect fit and finish across millions of units.
How does Apple test prototype durability?
Apple performs drop, bend, fatigue, and thermal tests on every prototype.
Each iteration undergoes:
-
Dimensional verification with CMM scanners
-
Thermal expansion analysis
-
Environmental wear simulations
-
Repeated assembly/disassembly tests
This ensures real-world performance before final approval.
Does Apple use 3D printing in its prototyping process?
Yes — Apple uses 3D printing for early concept models (for ergonomics and visualization).
However, functional prototypes and production-ready samples are made using CNC machining to achieve full material properties and aesthetic fidelity.
Where are Apple prototyping labs located?
Apple operates primary hardware prototyping facilities in Cupertino (USA) and supporting CNC labs in Shenzhen (China) near its major suppliers.
This global setup ensures seamless collaboration between design and manufacturing.
How does Apple achieve such consistent surface finishes?
Apple uses a combination of automated polishing, bead blasting, and anodizing to create uniform surface textures.
Every finish is tested under different lighting conditions to ensure color consistency and tactile perfection.
What lessons can other manufacturers learn from Apple prototyping approach?
-
Integrate design and manufacturing early in the process.
-
Use rapid CNC machining for functional validation.
-
Combine aesthetic and mechanical testing for better end-user experiences.
-
Prioritize sustainability and recyclability in materials.
Does Apple recycle prototype materials?
Yes — Apple reuses aluminum and titanium scrap from prototyping for new parts.
Through its closed-loop system, Apple recycles over 200,000 tons of aluminum annually, supporting its zero-waste manufacturing goal.
How does Apple prototyping impact its product design philosophy?
Apple hardware prototyping reflects its core belief:
“Great design isn’t just seen — it’s felt.”
Through iterative CNC development and detail perfection, Apple turns industrial precision into emotional experience.
What software supports Apple prototyping workflow?
Apple engineers and designers use:
-
Siemens NX – precision modeling and machining simulation
-
SolidWorks – mechanical design and assembly
-
Mastercam – CNC toolpath generation
-
In-house CAD/CAM systems – integrated with metrology data for fast feedback