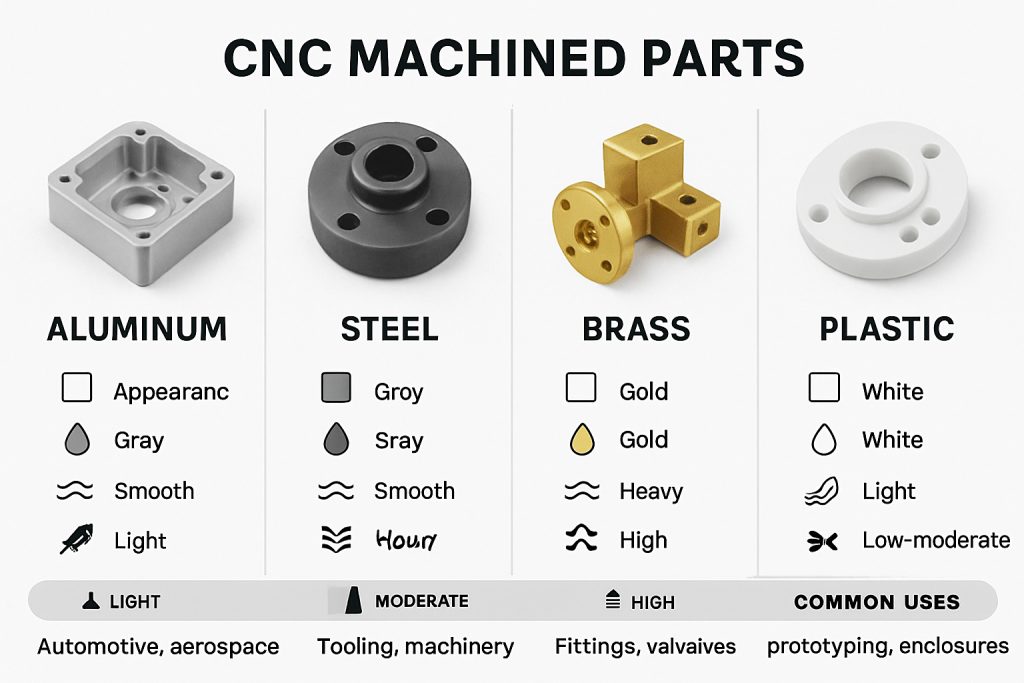
When it comes to CNC machining, choosing the right material is just as important as the design itself. The material you select will affect the part’s strength, durability, weight, cost, and overall performance. From lightweight aluminum alloys to high-strength titanium, each option has unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications.
In this article, we’ll explore the most common CNC machining materials, compare their properties, and provide a practical framework for making the best choice for your project. For an extensive selection of materials and machining services, you can explore the Boona Prototypes CNC machining services.
I. Overview of CNC Machining Materials
Metals
Boona Prototypes provides a wide selection of metals suitable for CNC machining, including:
-
Aluminum Alloys: 1060, 1100, 2017, 2024, 5052, 6061, 6063, 7075
-
Stainless Steel: 303, 304L, 316L, 410, 416
-
Steel & Tool Steel: AISI 4140, 4340, A2 Tool Steel, Alloy Steel
-
Titanium Alloys: Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-7Nb, Grade 23 ELI
-
Brass & Copper: C26000, C36000, Copper-Beryllium, Copper-Chrome
-
Other Alloys: Nickel, Inconel (IN718), Bronze, Magnesium (AZ31B, AZ91D, WE43)
👉 See full list on Boona CNC materials page.
Plastics
Engineering plastics are excellent alternatives to metals when weight reduction and chemical resistance are important:
-
ABS, Nylon, POM (Delrin), PMMA, PP, PVC, PEI, PEEK, PTFE, PC, PPSU, HDPE, LDPE.
Check more options: Plastic CNC machining services.
Elastomers & Silicone
For flexible parts:
-
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR), TPU, TPE, NBR, Viton (FKM), RTV.
II. Key Factors for Selecting the Right Material
| Selection Factor | Considerations | Example Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High loads, wear, impact resistance | Steel, Titanium, PEEK |
| Weight Requirements | Lightweight designs, drones, aerospace | Aluminum, Magnesium |
| Corrosion Resistance | Exposure to moisture, chemicals, or saltwater | Stainless Steel, Titanium, PTFE |
| Thermal/Electrical Needs | High heat resistance or conductivity | Copper, PEEK, Brass |
| Machinability | Ease of cutting, tolerance capability, surface finish | Aluminum, Brass, POM |
| Cost Efficiency | Balancing budget with performance | ABS, Aluminum 6061 |
III. Material Comparison Table
Here’s a comparison of common CNC machining materials and their properties:
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Machinability | Corrosion Resistance | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum 6061 | 2.70 | 310 | Excellent | Good | Aerospace brackets, automotive |
| Aluminum 7075 | 2.81 | 572 | Good | Moderate | Aerospace, defense |
| Stainless Steel 316L | 8.00 | 485 | Fair | Excellent | Medical, marine |
| Titanium Ti-6Al-4V | 4.43 | 900 | Difficult | Excellent | Implants, aerospace |
| POM (Delrin) | 1.41 | 70 | Excellent | Good | Gears, precision parts |
| PEEK | 1.32 | 100 | Fair | Excellent | Chemical pumps, aerospace |
| Copper | 8.96 | 210 | Excellent | Poor (oxidizes) | Electrical, thermal parts |
IV. Best Use Cases by Material
-
Aluminum (6061, 7075) – Best for lightweight structural parts, aerospace, and automotive components.
-
Titanium (Grade 5, 23 ELI) – Ideal for aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance engineering. See Boona Titanium CNC Machining.
-
Stainless Steel (316L) – Perfect for marine, food processing, and medical parts needing corrosion resistance.
-
Copper & Brass – Excellent for electrical conductivity and decorative finishes. More at Boona Copper CNC Machining.
-
Plastics (POM, PEEK, ABS) – Cost-effective, lightweight, and resistant to chemicals; useful in electronics, medical, and consumer products.
V. Tips for Choosing CNC Machining Materials
-
Define Application Requirements First: Mechanical load, weight, environment, and tolerance.
-
Balance Machinability and Cost: Aluminum and brass are cheaper to machine than titanium or hardened steel.
-
Consider Prototyping vs. Production: Quick-turn prototypes can use cost-effective plastics before scaling to metals.
-
Consult Experts: Companies like Boona Prototypes provide material guidance, tight tolerances (±0.01 mm), and certification support (ISO 9001, ISO 13485, IATF16949).
Conclusion
Selecting the right material for CNC machining is a balance of strength, weight, cost, and performance. Aluminum and plastics are excellent for cost-efficient prototypes, while titanium and stainless steel are essential for demanding industries like aerospace, medical, and marine.
With a vast range of materials and precision machining services, Boona Prototypes is a reliable partner for both prototyping and full-scale production. By aligning your design requirements with the right material properties, you can achieve optimal results in both function and cost efficiency.
FAQs
1. What is the most commonly used material for CNC machining?
Aluminum alloys, especially 6061 and 7075, are among the most widely used CNC machining materials due to their excellent machinability, light weight, and good balance of strength and cost. You can explore aluminum CNC machining services for versatile applications.
2. How do I choose between aluminum and titanium for CNC machining?
-
Aluminum is cost-effective, lightweight, and easy to machine—ideal for prototypes and automotive parts.
-
Titanium is stronger, corrosion-resistant, and biocompatible—perfect for aerospace and medical applications. See titanium CNC machining options for high-performance needs.
3. Are plastics a good alternative to metals in CNC machining?
Yes. Engineering plastics like POM (Delrin), PEEK, and ABS are excellent alternatives when weight reduction, chemical resistance, or electrical insulation is important. Learn more about PEEK CNC machining for advanced engineering applications.
4. Which CNC materials have the best corrosion resistance?
Materials like Stainless Steel 316L, Titanium alloys, and polymers such as PTFE and PEEK provide outstanding corrosion resistance, making them ideal for marine, chemical, and medical environments.
5. What is the cheapest material to machine with CNC?
Generally, ABS plastic, aluminum alloys (like 6061), and brass are the most cost-effective due to their machinability and availability. For budget-conscious projects, these materials reduce machining time and costs.
6. Can CNC machined parts be made from copper?
Yes, copper and brass are excellent CNC materials, particularly for applications requiring thermal and electrical conductivity. Explore copper CNC machining services for electronics and heat-exchange components.
7. What tolerances can be achieved with different CNC materials?
At Boona Prototypes, tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm can be achieved depending on the material. Metals like aluminum and brass are easier to machine to fine tolerances compared to harder materials like titanium or stainless steel.
8. How does production volume affect material choice?
For low-volume prototyping, plastics and aluminum are often preferred due to lower costs and faster machining times. For high-volume or mission-critical parts, stronger and more durable materials like titanium, stainless steel, or PEEK are better suited.
9. Can I switch materials between prototyping and production?
Absolutely. Many companies prototype in aluminum or ABS plastic for cost efficiency and later switch to titanium, stainless steel, or PEEK for production runs, depending on end-use requirements.
10. Does Boona Prototypes provide material certification?
Yes. Boona can provide material certifications and inspection reports (ISO 9001, ISO 13485, IATF16949) upon request, ensuring that your CNC machined parts meet industry standards.



