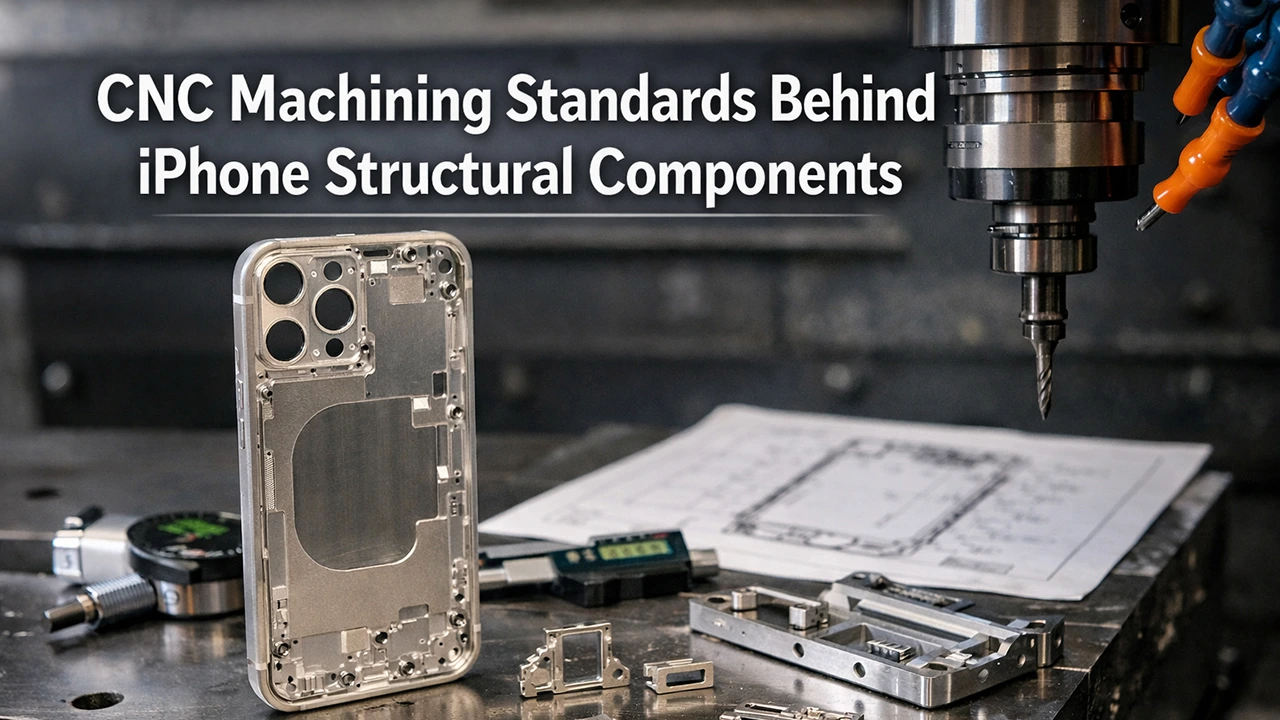
Apple iPhone is widely regarded as one of the most precisely manufactured consumer electronics products in the world.
Behind its seamless metal frame, tight assembly gaps, and exceptional durability lies a strict set of CNC machining standards that govern how every structural component is produced.
From unibody housings to internal frames and camera brackets, high-precision CNC machining plays a decisive role in achieving Apple-level quality at massive scale. This article explores the machining standards, tolerances, materials, and inspection processes behind iPhone structural components—and what manufacturers can learn from them.
Why CNC Machining Standards Matter in iPhone Manufacturing
Unlike plastic injection-molded housings, iPhone structural components are machined from solid metal billets, requiring:
-
Extremely tight dimensional tolerances
-
High cosmetic surface standards
-
Repeatability across millions of parts
-
Compatibility with automated assembly lines
Even a 0.02 mm deviation can lead to:
-
Assembly misalignment
-
Antenna performance degradation
-
Poor tactile feel
-
Visible cosmetic defects
This is why Apple relies heavily on advanced CNC machining standards, many of which exceed typical consumer electronics requirements.
iPhone Structural Components Manufactured by CNC Machining
CNC machining is used for both external and internal load-bearing components.
Key CNC-Machined Structural Parts
-
Unibody housing / mid-frame
-
Internal structural brackets
-
Camera module frames
-
Button housings and rails
-
Speaker grills and port structures
These components demand a combination of mechanical strength, precision fit, and cosmetic perfection.
International CNC Machining Standards Used in iPhone Production
ISO Standards for Precision Machining
Apple-aligned CNC suppliers typically follow international standards such as:
| Standard | Purpose |
|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality management system |
| ISO 2768 | General dimensional tolerances |
| ISO 1302 | Surface texture and roughness |
| ISO 14253 | Inspection and measurement rules |
These standards ensure global manufacturing consistency, even across multiple CNC facilities.
GD&T (ASME Y14.5) in Structural Parts
Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) is critical for parts like:
-
Camera frames
-
Logic board mounting points
-
Connector and port alignment
Common GD&T controls include:
-
Flatness
-
Parallelism
-
Position
-
Concentricity
These ensure precise assembly even under tolerance stack-up conditions.
Material-Specific CNC Machining Standards
Different iPhone generations use different structural materials, each with unique machining challenges.
Aluminum Alloy CNC Standards
Used extensively in standard iPhone models.
Typical parameters:
-
Alloy: 6000-series aluminum
-
Wall thickness: ≥ 0.6 mm
-
Flatness tolerance: ≤ 0.02 mm
-
Surface roughness: Ra ≤ 0.8 μm
Aluminum frames often undergo:
-
CNC roughing
-
CNC finishing
-
Sandblasting
-
Anodizing
Stainless Steel CNC Standards
Used in earlier Pro models for enhanced rigidity.
Challenges:
-
High tool wear
-
Heat accumulation
-
Surface polish consistency
Key controls:
-
Reduced cutting speeds
-
Multi-step polishing
-
Strict burr control
Titanium CNC Machining Standards (Pro Models)
Titanium introduces the most demanding CNC requirements.
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Dimensional tolerance | ±0.01 mm |
| Cutting speed | 30–60 m/min |
| Tool material | Carbide / coated |
| Edge radius | 0.05–0.1 mm |
Titanium frames require multi-axis CNC machining with thermal compensation to prevent distortion.
Precision Tolerances in iPhone Structural Components
iPhone structural parts operate within micron-level tolerance windows.
Typical Tolerance Ranges
| Component | Tolerance | CNC Process |
|---|---|---|
| Unibody mid-frame | ±0.02 mm | 5-Axis CNC Milling |
| Camera frame | ±0.01 mm | High-speed CNC |
| Button housing | ±0.015 mm | CNC Turning |
| Speaker grill | ±0.02 mm | Micro CNC Milling |
These tolerances are significantly tighter than those used in standard consumer electronics enclosures.
CNC Process Standards Applied in Apple-Level Manufacturing
To achieve these tolerances consistently, manufacturers use:
-
5-axis CNC machining for complex geometries
-
High-speed spindle systems (20,000–40,000 RPM)
-
Toolpath optimization to minimize vibration
-
Thermal compensation algorithms
At Boona Prototypes, similar CNC process controls are applied for high-precision consumer electronics prototyping and low-volume production.
👉 Learn more about advanced CNC machining services:
https://www.boona-prototypes.com/cnc-machining/
Quality Control & Inspection Standards
In-Process and Final Inspection
Apple-grade CNC production typically includes:
-
First Article Inspection (FAI)
-
Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) checks
-
Optical and laser scanning
-
SPC (Statistical Process Control)
Cosmetic inspection is often 100% manual for visible parts.
| Inspection Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| CMM | Dimensional accuracy |
| Laser scanning | Surface deviation |
| Visual inspection | Cosmetic defects |
| SPC | Process stability |
Clean Manufacturing & Environmental Standards
Structural iPhone components must meet clean manufacturing requirements:
-
Oil and particle contamination control
-
Chip-free cavities
-
Cleanroom-compatible packaging
Material traceability and sustainability standards are increasingly important, especially for global brands.
How CNC Standards Improve iPhone Durability & Performance
Strict CNC standards directly contribute to:
-
Higher structural rigidity
-
Improved drop resistance
-
Better heat dissipation
-
Consistent antenna performance
-
Seamless tactile feel
These benefits are difficult to achieve using casting or stamping alone.
CNC Supplier Requirements for iPhone-Grade Components
Suppliers must demonstrate:
-
Advanced CNC equipment capability
-
Stable tolerance control
-
Documented process workflows
-
IP protection and NDA compliance
For startups and OEMs, applying Apple-inspired CNC standards during prototyping can dramatically improve final product quality.
👉 Related: Rapid CNC prototyping for consumer electronics
https://www.boona-prototypes.com/rapid-prototyping/
What Manufacturers Can Learn from Apple CNC Standards
Even without Apple-level budgets, manufacturers can adopt:
-
GD&T-driven design
-
Early tolerance analysis
-
Prototype-to-production CNC consistency
-
Data-driven quality inspection
This approach reduces redesign cycles and accelerates time-to-market.
Conclusion: CNC Machining Standards as the Foundation of iPhone Design
The iPhone’s premium look, feel, and durability are not accidental—they are the result of rigorous CNC machining standards applied to every structural component.
From micron-level tolerances to advanced materials like titanium, Apple CNC requirements represent the gold standard for consumer electronics manufacturing.
By applying similar principles, manufacturers and product developers can significantly elevate their own product quality—starting from the prototype stage.
FAQs
Why does Apple use CNC machining for iPhone structural components?
Apple uses CNC machining because it delivers exceptional dimensional accuracy, surface quality, and structural strength. CNC-machined metal frames offer tighter tolerances, better durability, and superior cosmetic finishes compared to casting or stamping methods.
What CNC tolerance standards are typically used in iPhone structural parts?
Most iPhone structural components are manufactured within ±0.01 mm to ±0.02 mm tolerances. Critical areas such as camera frames and connector interfaces often require even tighter control to ensure proper alignment and assembly.
Which international CNC standards apply to iPhone manufacturing?
iPhone-grade CNC machining generally follows:
-
ISO 9001 for quality management
-
ISO 2768 for general tolerances
-
ISO 1302 for surface roughness
-
ASME Y14.5 (GD&T) for geometric tolerancing
These standards ensure global consistency and repeatable quality.
What materials are CNC machined for iPhone structural components?
Common materials include:
-
6000-series aluminum alloys for lightweight strength
-
Stainless steel for enhanced rigidity
-
Titanium alloys (Pro models) for high strength-to-weight performance
Each material requires different CNC parameters, tooling, and process controls.
Why is 5-axis CNC machining important for iPhone frames?
5-axis CNC machining allows complex geometries to be machined in a single setup, reducing repositioning errors, improving surface consistency, and achieving tighter tolerances—especially for curved edges and internal cavities.
How does CNC machining affect the cosmetic quality of iPhone housings?
CNC machining enables:
-
Uniform surface textures
-
Precise edge radii
-
Clean transitions between surfaces
This is critical for A-surface cosmetic areas, which must remain defect-free after anodizing, polishing, or coating.
What surface finish standards are used for iPhone structural parts?
Visible iPhone components typically require:
-
Surface roughness (Ra) ≤ 0.8 μm
-
Strict control of scratches, tool marks, and burrs
-
Consistent finish after secondary processes like sandblasting or anodizing
How are CNC-machined iPhone parts inspected for quality?
Quality control includes:
-
First Article Inspection (FAI)
-
CMM dimensional verification
-
Laser or optical scanning
-
100% visual inspection for cosmetic components
-
Statistical Process Control (SPC) for mass production
Why is tolerance stack-up critical in iPhone structural design?
Tolerance stack-up can cause misalignment between components, affecting:
-
Camera performance
-
Button feel
-
Assembly fit
-
Antenna functionality
CNC machining standards help minimize these risks by maintaining consistent dimensional accuracy.
Can non-Apple manufacturers apply similar CNC standards?
Yes. While Apple operates at massive scale, similar CNC standards can be applied to prototyping and low-volume production. Companies like Boona Prototypes help startups and OEMs achieve Apple-level precision during early development stages.
How does CNC machining improve iPhone durability?
High-precision CNC machining improves:
-
Structural rigidity
-
Drop resistance
-
Fatigue life
-
Heat dissipation
This results in a more robust device without increasing weight.
What should companies look for in a CNC supplier for high-precision electronics?
Key criteria include:
-
Advanced 3-axis and 5-axis CNC equipment
-
Proven tolerance control (±0.01 mm capability)
-
Strong quality inspection systems
-
Experience with consumer electronics materials



